|
A mobile phone is often used in a noisy environment.
When a speech signal mixed with noise is transmitted to a far-end talker, speech quality degrades. To suppress noise signals, we investigate a noise suppressor using a speech model which is a speech spectral amplitude PDF (probability density function). | 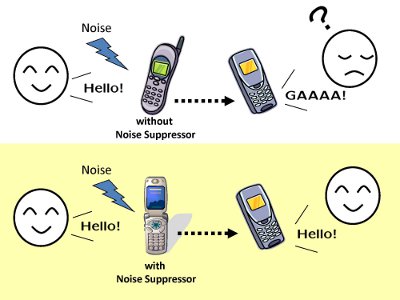 |
|
Let an observed signal be Y=X+D, where X is a speech and D is a noise, respectively.
When Y=1, X may not be "2" or "3". But, it is possible that X is around "0.5". The figure in the right hand side shows a speech PDF, where the horizontal axis denotes a speech value. In this case, we can choose an estimated speech signal as the value which gives the maximum speech PDF (it is 0.5 in this figure). When successively transmitting the estimated speech to the far-end talker, noise suppression is achieved. | 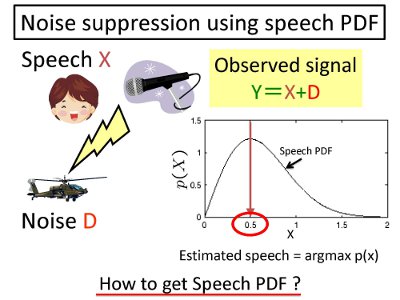 |
|
The speech PDF is the most important factor in this method.
Althogh many speech PDFs have been proposed, they represents an averaged speech model. We assume that the speech PDF depends on the present speech power. The proposed method changes the speech PDF by evaluating the present speech power (actually, changing shape parameters of the PDF). | 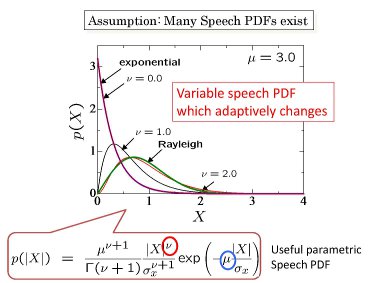 |
|
Spectrograms of noise reduction results.
The observed signal is a female speech mixed with a tunnel noise. Conv.1 employed a fixed speech PDF. Conv.2 employed a variable speech PDF which we previously proposed. The proposed method used a current variable speech PDF. The proposed method can strongly reduce the noise in comparison to the other methods. | 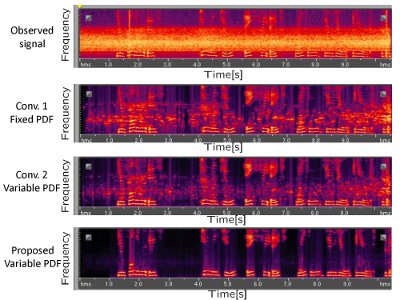 Sound Data |