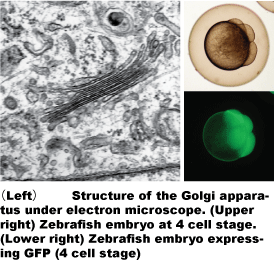
The Golgi apparatus is situated at the center of the vesicular transport pathway. It is an organelle where secretory and membrane proteins and some glycolipids are synthesized and modified. The Golgi apparatus inspects the quality of the synthesized and modified proteins and only the approved proteins are selected, sorted and dispatched to their final destinations. Our recent experimental results indicated that the Golgi apparatus plays important roles in the cell differentiation and polarization during the cell growth, death and tissue development.
It is proposed that the cell somehow monitors the functional state of the Golgi apparatus and efficiently regulates its localization and structure according to the needs of cellular functions. However, the regulatory mechanism has not been well understood. We, therefore, trying to elucidate (1) the molecular mechanism of the maintenance of the Golgi structure and its relationship with the cell cycle control, (2) the mechanism of the signal transduction from the Golgi apparatus to the cytoplasm and the nucleus, by analyzing the functions and dynamics of the proteins which are propose to be involved in the cell cycle control, cell movement and cell death using biochemical, molecular, cellular and developmental biological methods.
We are also trying to find (3) the role of the Golgi apparatus in the expression of the higher ordered cellular functions during embryonic and tissue development using zebrafish, which is suitable for the observation of embryogenesis and cell biological analyses, as a model organism. Especially, we are focusing on the dynamics of the Golgi apparatus and the associated proteins during the early embryogenesis to understand the role of the Golgi apparatus in the cellular morphogenesis and movement.
