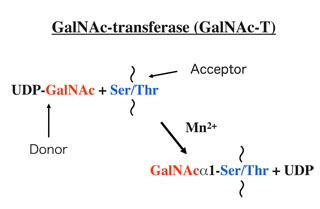
O-Glycosylation is an important post-translational modification of proteins, and is classified into several subtypes based on the carbohydrate-protein linkage structures. GalNAcα1->Ser(Thr) is the most frequently observed linkage, and O-glycans with this structure are called the mucin carbohydrates since they are highly expressed on mucins secreted from epithelial cells. There is another O-glycosidic structure, Manα1->Ser(Thr). Contrary to the mucin sugars, the occurrence of O-mannosylated carbohydrates is mostly confined to the tissues, such as muscle and brain. Our interest is to define functional roles of these two types of O-glycosylation in the brain, and we carried out the following experiments.
- 1) Analysis of synthesis and function of neuron-specific mucin-type carbohydrates
-
a UDP-GalNAc: polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyl- transferase (GalNAc-T) catalyzes the initial step in the biosynthesis of mucin-type glycans. We previously cloned a novel neuron-specific isozyme, designated GalNAc-T9, and more recently identified a putative GalNAc-T gene, which is also mainly expressed in the embryonic and adult brain. The gene for this putative isozyme is also known as WBSCR17, one of the genes identified in the region critical to Williams- Beuren syndrome (WBS). We carried out biochemical characterization of WBSCR17, and knockdown of brain- specific isozymes (GalNAc-T9, -T13, and WBSCR17), and obtained the following data.
- WBSCR17 was predominantly expressed in the cis-Golgi as is the case with other GalNAc-T isozymes, when its recombinant molecule with GFP was expressed in mammalian cells. The subcellular localization suggests that WBSCR17 may work as a glycosyltransferase.
- Carbohydrate profiles were studied in the cells with constitutively expressed WBSCR17 by metabolic labeling of carbohydrates using GalNAz. The detection of metabolically labeled glycoproteins from the cells with overexpressed WBSCR17 demonstrated bands with enhanced expression, indicating the possible glycosylation by WBSCR17.
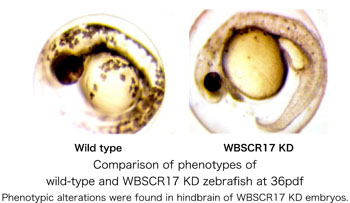
- The knockdown (KD) of WBSCR17 in zebrafish generated most severe malformation of hindbrain compared with the other brain-specific isozymes. We then examined the expression of some hindbrain markers, and found that wnt1 and rfng were lost or ectopically expressed. The KD of either wnt1 or rfng in zebrafish showed the similar phenotype to that of the WBSCR17 KD embryos. All these data indicate the WBSCR17 is somehow related to signal transduction of wnt1 and/or rfng.
- 2) Analysis of functions of O-glycosidic carbohydrates in α-dystroglycan (αDG)
-
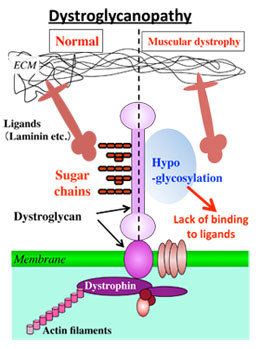
The aim of this project is to identify GalNAc-T isozymes involved in mucin-type O-glycosylation of αDG, and to identify the roles of αDG mucin-carbohydrates. To express FLAG-tagged αDG in zebrafish, we generated its construct. We are introducing the construct into the embryos.




